Saturday, August 22, 2009
Evolution Revision Questions and Answers
Revision Evolution MC Question 1
Revision Evolution MC Question 2
Revision Evolution MC Question 3/4
Revision Evolution MC Question 5
Revision Evolution MC Question 6
Evolution Revision MC Question 7
Revision Evolution MC Question 8
Answers
Revision Evolution MC Answer 1
Revision Evolution MC Answer 2
Revision Evolution MC Answer 3/4
Revision Evolution MC Answer 5
Revision Evolution MC Answer 6
Revision Evolution MC Answer 8
Revision Evolution MC Question 9
Thursday, August 13, 2009
Monday, August 3, 2009
Friday, July 31, 2009
History of Magnetism
800 BC - Greek peasants began using iron nails in their shoes, a shepherds shoe got stuck on a naturally occurring magnet, ancients believed that all magnets were attracted to this shepherds mountain in the province of Magnesia.
For over a thousand years Greeks made money by selling load stones
1585AD - Dr Gilbert (Queen Elizabeth I doctor) researched Amber (fossilised tree sap)(electrons) and the famous Dr Gilberts Balls were made out of magnets and he presented them to Queen Elizabeth I. He proved the earth was a giant magnet
Around 1785 - They found currents in wires made magnetic fields are wires with currents jumped in magnetic fields
Lesson on Resistance and Power

Thus they have the same brightness. Power loss can be calculated by working out the total resistance, the current and voltage drop and then the Power loss.
Wednesday, July 29, 2009
Tuesday, July 14, 2009
Monday, July 13, 2009
Evolution Experiment
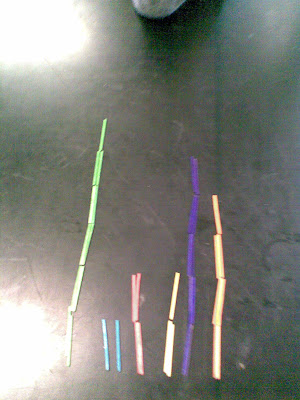
A start population 120 coloured tooth picks. Consisting of 6 colours of 20 sticks each.
The 120 were dispersed over a 15 x15 m area.
Two student preditors collected 10 sticks each.
From the kills the field population was calculated.
The field number divided by 5, was the number off spring that were generated and added and distributed to the field population.
In the sequence
Species - Sticks
Trait - Colour
Variation - Yellow, Orange, Red, Blue, Green,Purple
Selection - Not being Predated
Reproduction
Evolution.
We had predation out strip replacement due to over efficient predation.
The photo shows the final population after 7 seasons, havested from the field.
Friday, July 10, 2009
Tuesday, June 30, 2009
Thursday, June 25, 2009
Prac Assessment

Write an Aim, Propose a circuit with a two resistors, various voltmeters and ammeters.
Build and test the circuit, demonstrating these points.
Leave a space in your prac books to paste these points in.
Revision links
Basic circuits
Voltage
Series and Parrallel
Tuesday, June 23, 2009
Wednesday, June 17, 2009
Saturday, June 13, 2009
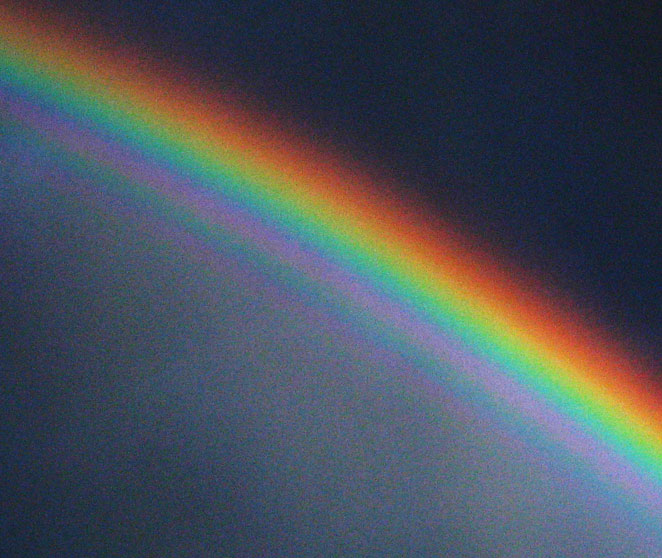
More on rainbows




Dr Hill Discusses Rainbows

Rainbows occur when sunlight is refracted as it enters, totally internally reflects and finally leaves water drops suspended in clouds.
The water drops have to larger than normal cloud droplets. Light from the background comes straight to you with out being scattered as it would be for fog or a cloud.
There are different colours because the red light travels faster through water, is refracted less and is at the top of the rainbow. Blue slows more and is bent further.
Because rainbows are reflected light you can enhance them with polaroid sunnies or completely turn them off by turning your sunnies through 90 degrees.
As you can see in the first photo there is a second more dispursed rainbow as the light takes a trip throught the rainbow.
You can also see repeated rainbows ans general cloudiness beneath the rainbow.
Friday, June 12, 2009
Saturday, June 6, 2009
Homework Register
14. Start of Term 3 - Holiday Homework
13. 8/7/09 Chapter 6 Questions 26 - 32. to be worked through in class - email questions you want worked through
12. 6/7/09 Page 117 questions 4 to 16 in Jacaranda Preliminary Course Physics
11. 2/7/09 Getting Electricity into the Home
10. 29/6/9 Prac assignment - Prelim work
9. 25/6/9 Complete writting the Galvani and Volta Debate - Dates- What they thought, what was the real answer. What does this say about the history of science.
8. 25/6/9 Complete Topic Test on The World Communicates
- Page 26 Q 14 , 15 Superposition of waves
- Write the speeds of sound for in air, water and vacuum, the speed of light
- What is the wavelength of 330 Hz sound
- Summarize the properties of IR, Vis, UV, Xrays, Gamma Link
- Question 13 Page 42
- Summarize Chapter 4 (8/6/09)
- Work Sheet on Motion (9/6/09)
Wednesday, June 3, 2009
Wednesday, May 13, 2009
Exam Notification
Homework For monday Upload a file of EM penetration.
2008 Exam will be handed in Tuesday, Scanned and corrected.
.
Monday, May 11, 2009
Thursday, May 7, 2009
Superpostion of waves
Friday, May 1, 2009
Wednesday, April 8, 2009
Holiday Homework
All questions on Page 10 and 11
Summarize Chapter 2
All question on Page 25 -26
Transverse Waves-1
Reflection and Refraction of Light Waves (Huygens' Principle)
Math, Physics, and Engineering Applets
PhET Wave Interference - Electric field, Interference, Diffraction ...
Thursday, April 2, 2009
Tuesday, March 31, 2009
Fun on Computers
Also down load http://audacity.sourceforge.net/download/windows audacity to see and hear your own voice in waves.
This program teaches Waves http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/wave-on-a-string/wave-on-a-string_en.html
High speed camera showing the critical middle bit of a collision where the kinetic energy is stored in the deformed golf ball before it springs away. Note also that the golf ball springs away with near twice the velocity of the golf club
Monday, March 30, 2009
Thursday, March 26, 2009
Kinetic energy in Collisions
Impulse = Ft = mat = m(u-v)/txt= m(u-v) = change in momentum
Impulse has units of Ns and momentum kg.m/s
Wednesday, March 25, 2009
Collisions
A collision is broken into three parts,
- heading towards each other (N1),
- touching, scrunching, and restoring (N3) and
- heading out from each other (N1)
the collision dynamics, or how step 1 leads to step 3 is in the detail of step 2.
TIME - MOMENTUM
In the actual collision the body one and two feel equal but opposite forces for duration of time.
Considering each body (N2) we have F2->1. t = ma1.t for what happens to body 1
and F1->2. t = ma2.t. Use N3 and the formulae v-u =at to derive conservation of momentum (p)
p1= m1.v1. Conservation means momentum before = momentum after.
DISTANCE - Energy
The collision first through a scrunch deformation stage where KE is converted to mechanical deformation. If the mechanical deformation is springy or elastic, the mechanical deformation is PE (potential energy) that then explodes the particles appart. (PE restore KE).
So unlike momentum the direction matters, and the light object travels a greater distance, loosing more and gaining more KE. The maths is tricky so you will only deal with case of objects colliding and sticking together- Completely inellastic collisions.
Homework: Question 10 and 11 page 244 Jacaranda HSC science.
Thursday, March 12, 2009
Thursday Lesson
You are to go to this link and workthrough the worksheet. I will check your books tomorrow.
You are to email me peter.hill26 reporting the progress on your assignment. Due next Tuesday
Remember - Discussion of Newton
-first law objects continuning motion
-Second law bodies decelerating and having forces(spreading the force)
-third law systems transfering momentum, Changing a lethal short impulse (Ft) to a non-lethal force (fT).
Remember - Evidence of the effectiveness of the device. Follow marking guideline.
Wednesday, March 11, 2009
Wednesday, March 4, 2009
Tuesday - Wednesday Prac

Monday, March 2, 2009
Wednesday, February 25, 2009
Wednesday Lesson
Y11HW Summarize Chapter 10 - 1 Page. Prepare for Prac 10.1 on page 221 with book ruled up
We will look at Vector components and acceleration using Tracker. You can download it from R drive, science, yr10, physics. It will greatly assist in performing pracs
Turn vectors into scalar (projections) then back into vectors.
- Each V has projections Vxx and Vyy where x and y "Unit vectors along the axis"
Newtons Laws 1-2-3
N1 Straight line, constant velocity (Speed and Direction), if F = 0
Historical: Break with Archemedies and common sense.
Application: Cars thrown through the window
N2 Sum of Forces = Resultant Force = Mass x Acceleration. (on a body)
Historical: Invention of Mass a number to link Force (that can be felt) and acceleration (that can be seen)
Application: Anything that moves, Constant velocity means NET force is zero.
Types of Forces
Internal- Generated by a Field generated by a body at distance Force just dropped on to object. - Gravity
External - Generated by contact , two forces generated. In sum only add the forces acting on it. Strings and Friction
N3 Every force has an equal and opposite force. (in a system)
Historical: Invention of Momentum, Impulse fT or Ft, ease up or death.
Application: Collisions, Lethal force
Friday, February 20, 2009
Homework
Homework now complete to Q25
In Class we cover Q 20 and how the area under a VT curve is the displacement , the gradient is the acceleration.
We are now in a position to Revise Newtons 3 Laws:
N1: With no forces, their velocity is unchanged.
This is historical reference to the different ideas of Aristotle of Violent, and curved motion.
N2: Sum of forces = product of acceleration and mass
Here the idea of forces need to be developed. Internal forces are found the product of an external field and an objects field force factor. For gravity the field is described by g and the number inserted to create the force is the Mass. In this case we draw the force on the object, determined by the field direction and the size by the size of the field and multiplier factor. The are also external forces mostly generated by strings or by contact with surfaces. Here we draw pairs of forces at the point of contact.
The sum of forces = a resultant force, ie a single force that does not add up. and this is the acceleration.
N3 F12=-F21 for every force there is an equal and opposite force. In the case of internal forces where the force vector is inserted, there is an opposite force but it is just not on the diagram. For contact forces we draw a pair of forces that cancel. This law basically leads to the concepts of momentum transfere, and the conservation of momentum as the forces balance.
Friday, February 13, 2009
Friday Lesson
Did intital Moodle- test and discussion on assignment.
Homework - Q8,Q9,Q10.
Thursday, February 12, 2009
More Vector Maths
Here is a good interative site
This lesson we will take a fast and slow ticker tape, the slow represents current that travels N, S,W,E and you will have to find the Vector necessary to travel N.
We will reveiw Q5 on page 194 Jacaranda and set Q6 for homework.
Monday, February 2, 2009
Vector maths
1) Drawing the vectors
2) breaking into X an Y components, adding Scalars, and recombining answers.
A good site with worked solutions for vector subtraction is site
Homework
distance- is between point a and b is the length of path pulled out straight(depending on the path)
= to a magnitude and unit this is a SCALAR
Displacement: is the chance in place as the "crow's flys"
= to a magnitude, unit, and direction this is VECTOR
it is draw in the diagram with an arrow. the Head is where it finishes, the tail is where it begins.
It is drawn to scale, and direction.( Diagram now needs a compass or an up)
The unit and magnitude is written half way along.
Vector addition is more complex than Scalar.....
Exercise Draw the Vector C , A+B =C
A is 8 paces north, B is 6 paces west.
Exercise Vector D Sum of ( 3 m North, 5 m East, 5 m South, 7 m West)
Exercise Vector E (Sum 7 m West, 5m South, 3 m North, 5 m East)
How do you subtract vectors? ANS go the opposite way
Exercise what is A - B ? Hint A + (-B).
Wednesday, January 28, 2009
Homework 28 Jan
Domain: knowledge and understanding:
Refer to the Science Years 7–10 Syllabus for the following:
5.6.2a) describe qualitatively the relationship between force, mass and acceleration
Force can be felt, Acceleration felt and observed, Newton invented the idea of mass as a mathematical link between force and acceleration, and the link explaining the gravitational forces between object. Mass is a mathematical value attached to an object. (Einstein also linked Mass with Nuclear Energy and there is also one further link of mass in Quantum Mechanics)
Write the equation linking Force , Mass and Acceleration.
If you were had a paddle that applied the same amount of force every time you used it. Describe how quickly you could accelerate in a Kayak that had:
a) Just you in it
b) You and a Polar Bear
5.6.2b) explain qualitatively the relationship between distance, speed and time
What two things do you need to measure speed?
Explain the “Hare and the Tortoise”
5.6.2c) relate qualitatively acceleration to change in speed and/or direction as a result of a net force
Explain what is happening in an arm wrestle.
5.6.2d) analyse qualitatively common situations involving motion in terms of Newton’s Laws.
Research Newton’s 3Laws –
Qualitatively Explain
N1: why holding a child in the front seat is not safe
N2: an arm wrestle
N3: why a punch hurts
Tuesday, January 27, 2009
First lesson
Your eBook is Excel we start with Moving about
This is a link to the eSyllabus
Calander
Translator
About Me

- drhill
- I come from a Science family: My father Geoffrey Hill was Australia's first computer programmer on CSIRAC the fourth computer in the world. He is credited with invention of Computer music and the development of “Interprogram” a language before Basic. My PhD is in Atomic and Molecular Physics. I have researched the activated oxygen layer above the ozone layer, and 'Assigned' the world's smallest molecule. At the University of Toronto I researched high power UV lasers. I have specialized in automation in fibre optics. This developed into research in Machine Intellect and Robots. I have enjoyed work as an Explainer with Questacon and my time as a part-time soldier. I currently teach High School Science at Epping Boys’ High.















